GUILLAIN-BARRÉ SYNDROME (GBS)
Understanding GUILLAIN-BARRÉ SYNDROME (GBS) & its impact on hand function & recent outbreaks.
In this article, Dr. Madhusudhan, a renowned hand, wrist, and microvascular surgeon, discusses the recent Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) outbreak in India, its implications for hand function, and the critical role of timely treatment and surgical interventions in recovery.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare, autoimmune condition that affects the peripheral nervous system, leading to acute muscle weakness, sensory disturbances, and, in severe cases, paralysis. Recent reports of a Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) outbreak in India, including cities like Bangalore and Pune, highlight the urgent need for awareness, prompt treatment, and specialized care.
GBS: An Overview and Implications for Hand Function
Acute Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) typically manifests with ascending paralysis, starting in the legs and progressing to the upper limbs. For hand surgeons, the disease’s impact on hand function is particularly relevant, as patients may experience loss of grip strength, fine motor skills, and even sensory deficits. Without timely management, complications like contractures and deformities can develop, further affecting the wrist and hand.
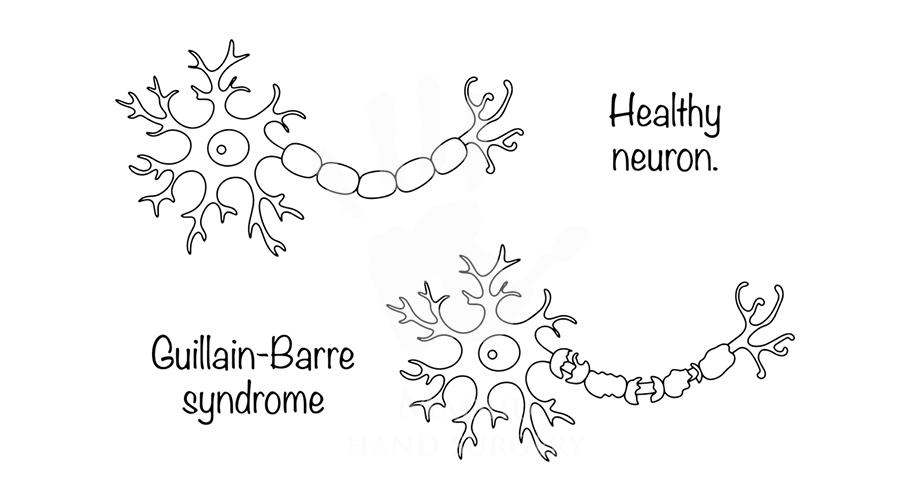
- Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (AIDP) – The most common type, involving damage to the myelin sheath.
- Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN) – Primarily affects motor nerves, often seen in younger patients.
- Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN) – A severe variant with motor and sensory nerve involvement.
- Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS) – A rare subtype affecting eye muscles, with potential hand coordination issues.
Treatment Modalities:
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) treatment focuses on halting the immune attack and supporting recovery. The main interventions include:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) – A critical care treatment to neutralize harmful antibodies.
- Plasmapheresis – Helps remove the antibodies causing nerve damage.
- Supportive Care – Includes ventilatory support in severe cases and physical therapy for muscle recovery.
- Rehabilitation Surgery – Hand surgeons may be involved in tendon transfers or managing contractures in chronic GBS cases.
Addressing Common Concerns About GBS:
While Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cannot be transmitted from person to person, it often follows infections such as campylobacter or viral illnesses. Kids can develop Guillain-Barré Syndrome, although it is more common in adults. Although rare, GBS can cause death due to respiratory failure or cardiac complications. However, with advancements in critical care, most patients survive GBS, and many achieve significant disease recovery.
The Current GBS Outbreak in India
The Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) outbreak in India, particularly in Bangalore and Pune, has raised concerns about potential triggers, such as infections or environmental factors. Outbreak management involves early diagnosis, public awareness, and access to acute care facilities. Timely treatment significantly improves outcomes, reducing the risk of death from Guillain-Barré Syndrome and ensuring better recovery.
A Hand Surgery Perspective
As a hand, wrist, and microvascular surgeon, the role extends beyond treating mechanical complications. Collaborative efforts with neurologists and rehabilitation experts are vital for restoring hand function. Surgical interventions, such as managing tendon contractures or nerve decompression, may be necessary for patients with severe or prolonged deficits.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a challenging disease condition, but it is not without hope. While it cannot be entirely cured, early intervention and comprehensive care significantly enhance recovery. This outbreak serves as a reminder of the importance of vigilance and collaboration in managing rare but impactful conditions.